Arc Routing Problems with Time Duration Constraints and Uncertainty
Texte intégral
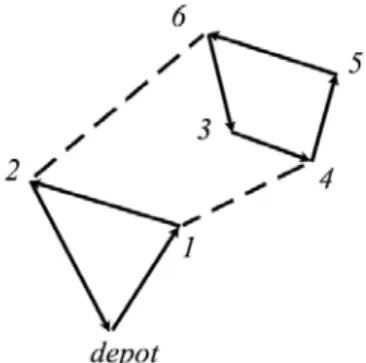
Figure
Documents relatifs
Our main contributions are (i) the study of techniques to reduce the number of extreme points of the uncertainty polytope that must be considered in the model, and (ii)
Among these methods, two population-based algorithms (MEANS [34] and Ant-CARP [32]) and one local search algorithm (GLS [2]) represent the state-of-the-art solution methods for
A feasible loading is defined as follows: first, it must satisfy the packing con- straint, items cannot overlap each other and they must fit completely into the vehicle; second,
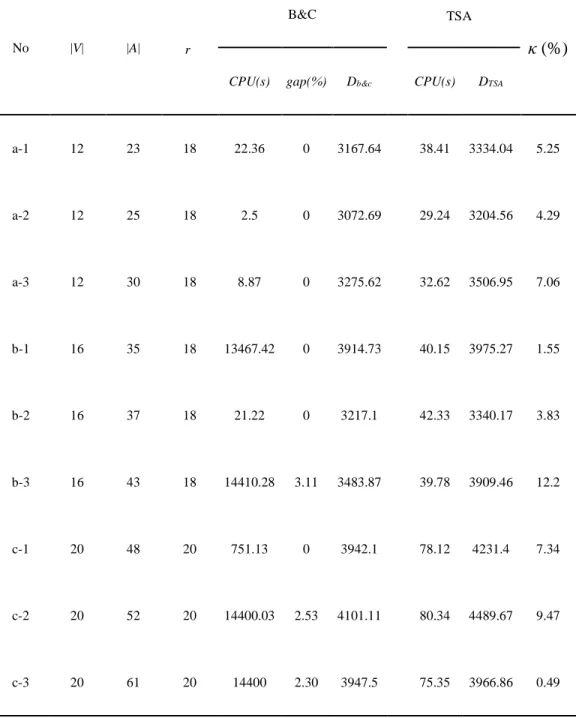
For each instance, Table 2 shows the number of vehicles, total route cost (service cost plus travel cost), and CPU time in seconds to reach the best solution with VND.. The last
Our results also show that the new exact algorithm based on this lower bound is competitive with the best known ones, and can solve to optimality 27 previously unsolved instances
We also propose a MIP-based constructive heuristic for the CEARP on directed- and mixed- graph instances based on the formulation of [6] in which the large number M is bounded
For routes with stochastic items, a packing problem is solved for every possible scenario to calculate the exact recourse cost of the route and generate a D-optimality cut (40) if
The FSMLRPTW consists of opening a subset of depots, assigning customers to them and determining a set of vehicle routes such that all vehicles start and end their routes at