Small spatial scales in wetting on non-structured and structured surfaces: thin films of liquid crystals & small-scales wetting properties of ionic liquids
Texte intégral
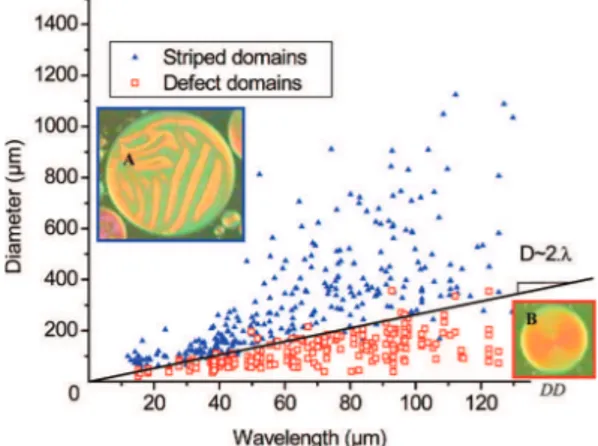
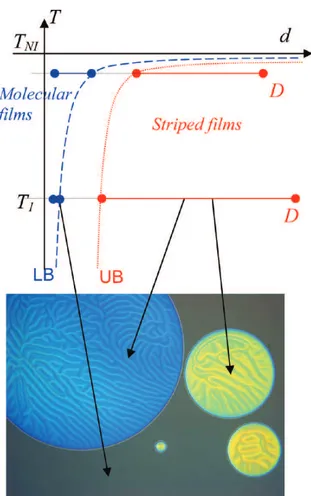
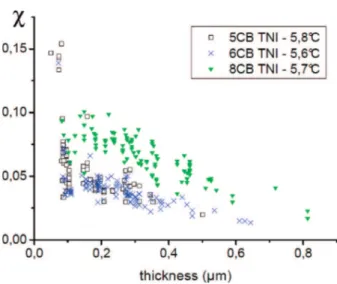
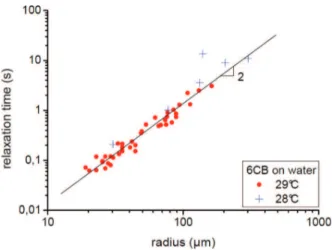
Figure

Documents relatifs
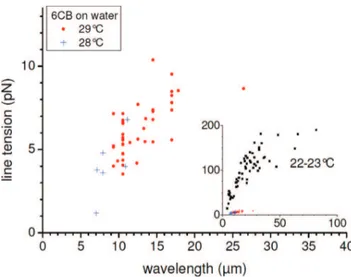
The role of the transition zone between the wetting films and bulk liquid in the phenomena of line tension, mechanical and thermodynamical equilibrium, and the
of fluctuation effects close to the transition point. This suggested examination of the effect of fluctuations close to the instability threshold [11,12]. The main step
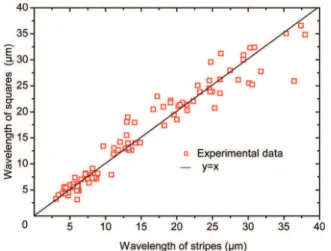
It is shown that these oscillations can play an important role in determining the thermodynamic stability of a wetting layer, close to the critical point of a binary
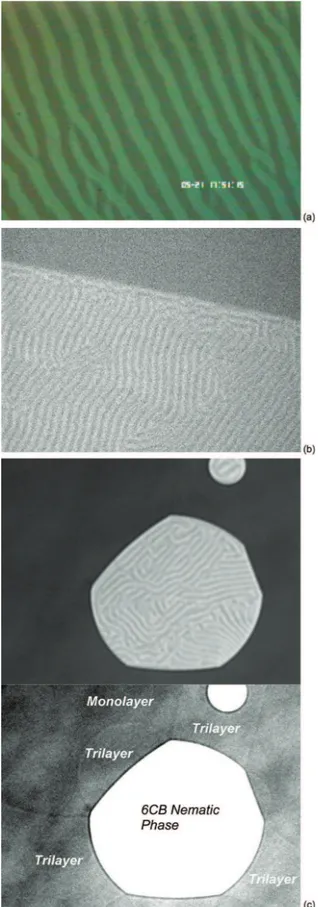
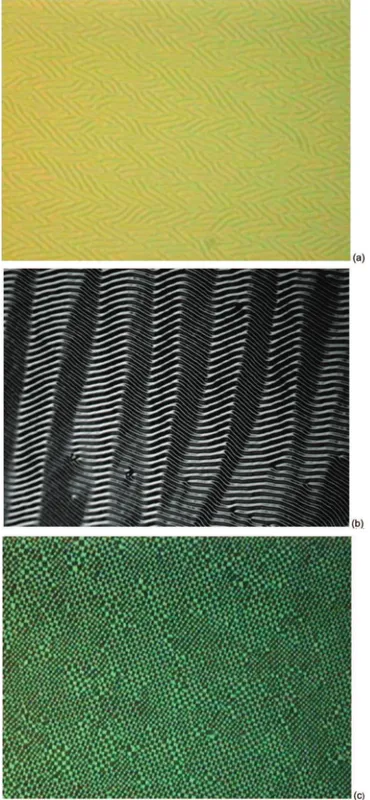
The process for the production of the light polarizing films consists of rubbing a glass or plastic surface substrate with a water slurry of a rouge in the direction or
shows the volume versus the time remaining for the drop to evaporate completely for all the experimental runs; (b) global evaporation rate versus the radius again after averaging
For phosphors with a relatively large doping of luminescent ions, the saturation effect caused by an intense excitation density must be taken into account in interpreting
Presumably the acoustical attenuation arises from coupling of sound waves with both fluctuations of the director and magnitude of the order parameter. Unfortunately it is
Edge dislocation in a vertical smectic-A film: Line tension versus temperature and film thickness near the..