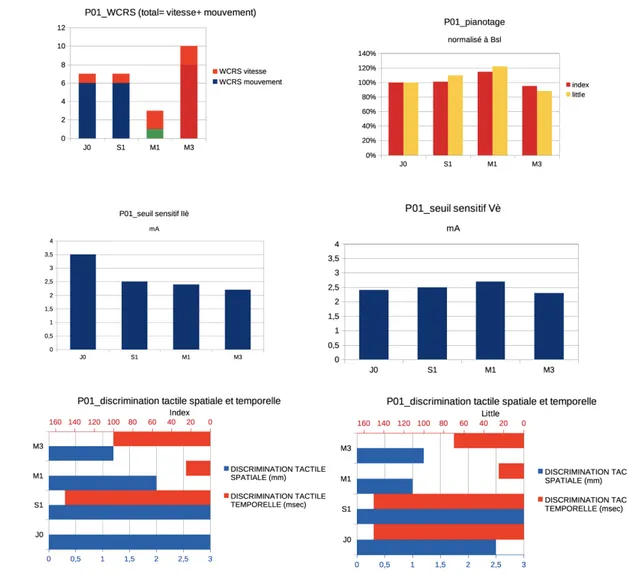
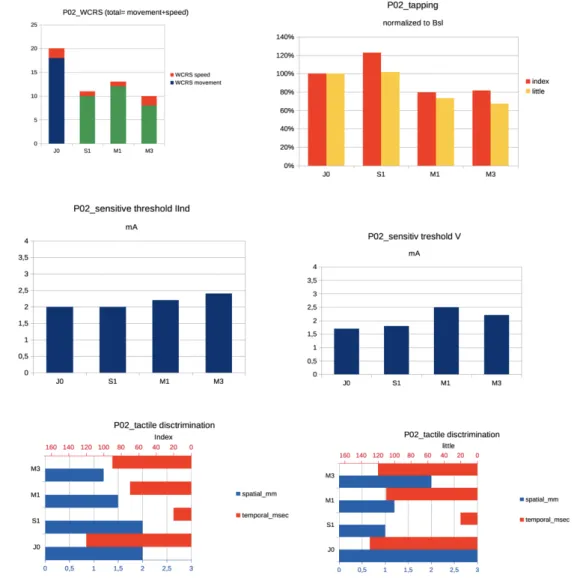
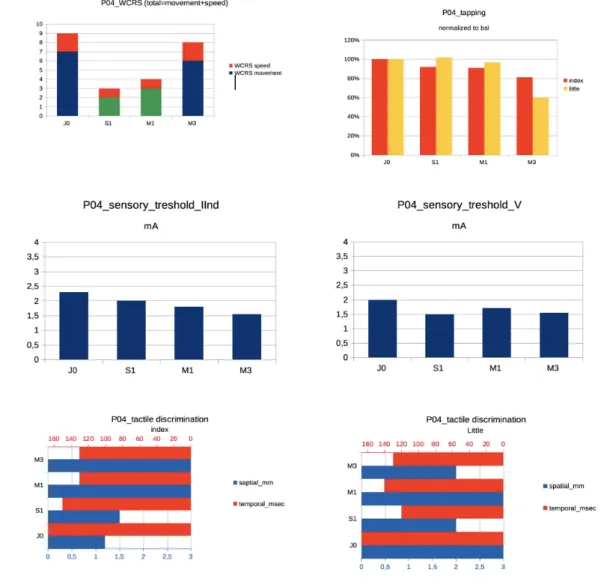
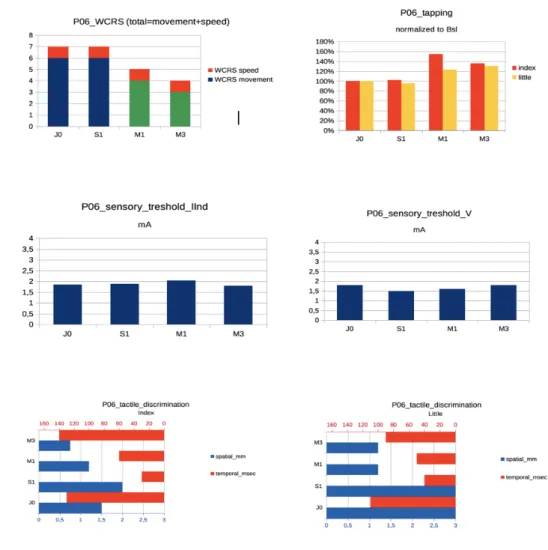
Exploring central nervous system effects of peripheral botulinum toxin injection in writer's cramp patients using transcranial magnetic stimulation
Texte intégral
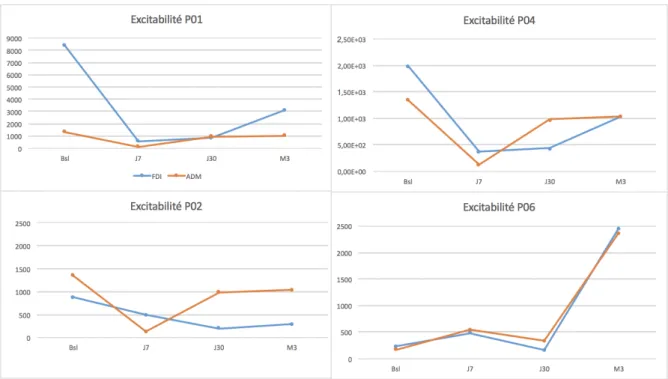
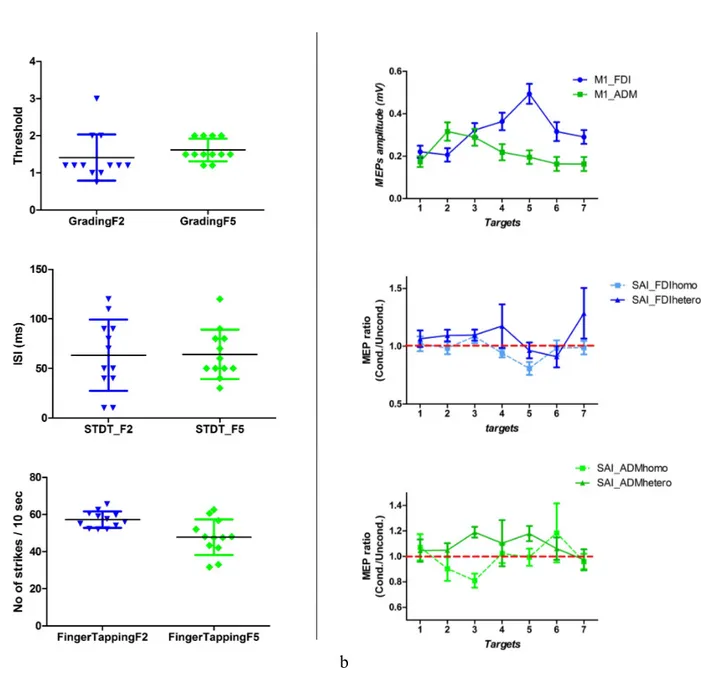
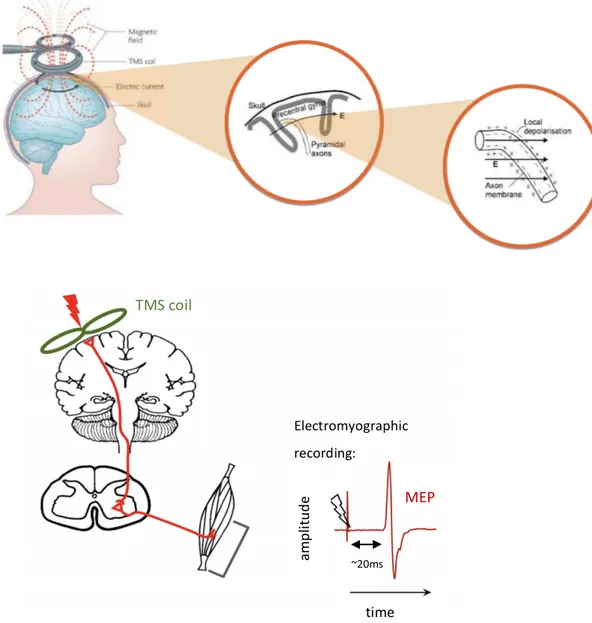
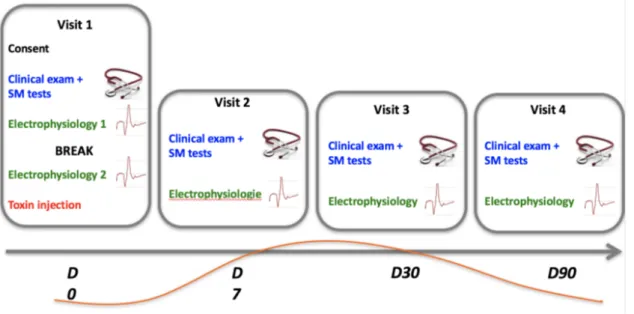
Figure
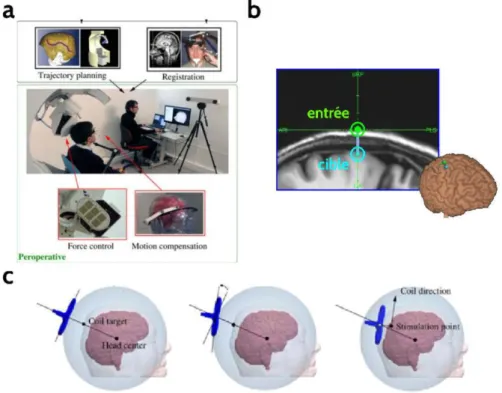
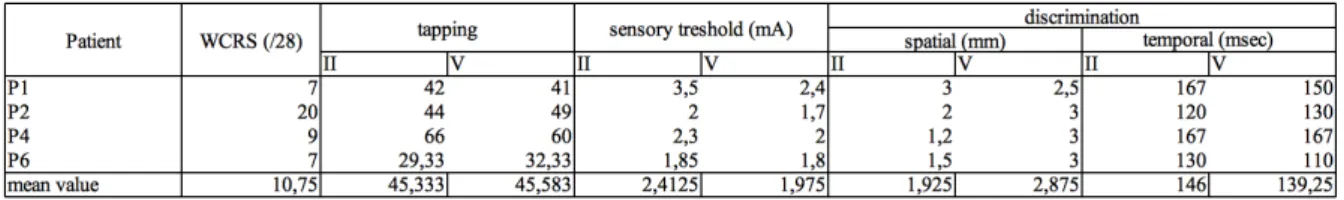
Documents relatifs
At the left hind limb, muscle surface area, cor- tical thickness, cross sectional total area and growth in length signi fi cantly increased during the time study.. At the right
(11) showed that BTI injection in the RF muscle significantly improved peak knee flexion in the swing phase of the gait cycle, but tended to improve only the 10-m walking test,
At the left hind limb, muscle surface area, cortical thickness, cross sectional total area and growth in length significantly increased during the time study.. At
In the present study, we investigated for the first time the potential direct analgesic effects of one-time BTX-A in the painful area in patients with focal
Efficacy of injections of botulinum toxin-A for improving drooling and quality of life in disabled patients.. Beranger T, Pierache A, Loffer Z, Tiffreau V, Ferri J,
The aim of the present study was to investigate long term effects of motor denervation by botulinum toxin complex type A (BoNT/A) from Clostridium Botulinum, on the afferent
OBJECTIVE: The aim of this study was to analyze the effects of botulinum toxin (BT) injection on airflow stability, by measuring mean phonatory oral airflow and its coefficient
Afferented central EVC in the normally sighted exhibited a positive FC with the bilateral inferior and middle occipital and bilateral posterior part of the lingual gyri,