Classical and quantum out-of-equilibrium dynamics. Formalism and applications.
Texte intégral
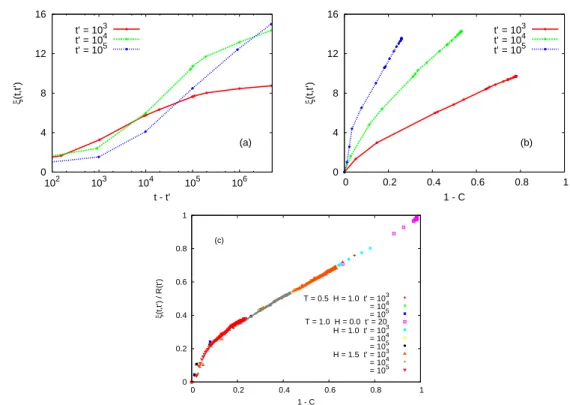
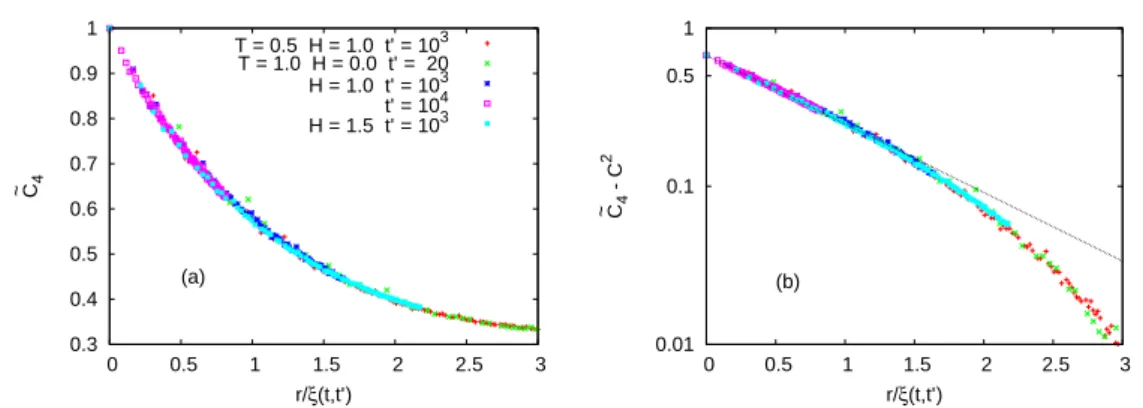
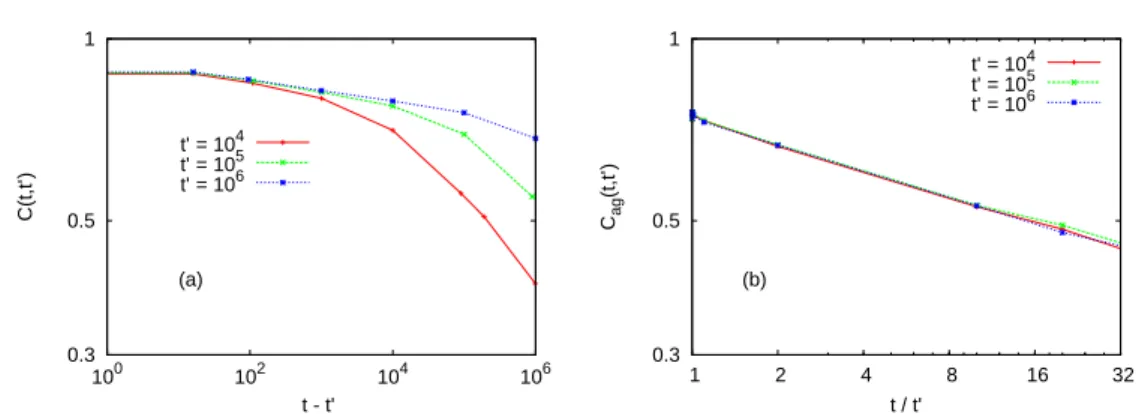
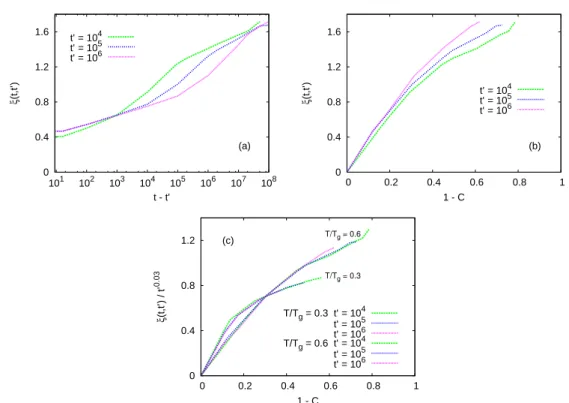
Figure
Documents relatifs
In this section, we focus on the ohmic spinboson model and investigate how the interaction with the bath triggers at high coupling a quantum phase transition from a delocalized to
Classical teleportation is defined as a scenario where the sender is given the classical description of an arbitrary quantum state while the receiver simulates any measurement on
The quantum -machine Q0 = q , Ω0 , M0 is an optimal quantum model for the 1D Ising spin chain, and hence its internal entropy Hρ corresponds to the quantum statistical complexity Cq
In 1977, Chirikov and his collaborators proposed the kicked rotator as a quantum model for Hamiltonian chaos, and showed that quantum effects limit the classical
Constructing quantum dissipations and their reversible states from classical interacting spin systems.. Annales
in classical and quantum statistical mechanics it suffices to postulate the grandcanonical distributions and that the other two, the canonical and the.. microcanonical, can
This allows us to reveal the classical-quantum duality of the Schwarzschild-Kruskal space-time: exterior regions are classical or semiclassical while the interior is totally
The upper panel shows, as a function of the cooling rate, the measured correlation length when reaching the critical point; the dashed line is its predicted evolution (see eq..