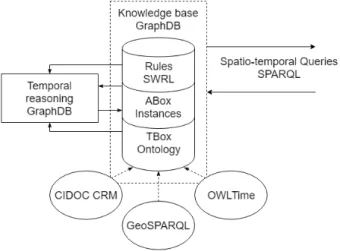
Spatio-temporal reasoning in CIDOC CRM: an hybrid ontology with GeoSPARQL and OWL-Time
Texte intégral
Figure


Documents relatifs
The assessment of the interactions of radionuclides with stable pollutant was carried out using ANOVA to test for significant differences between reference and stable
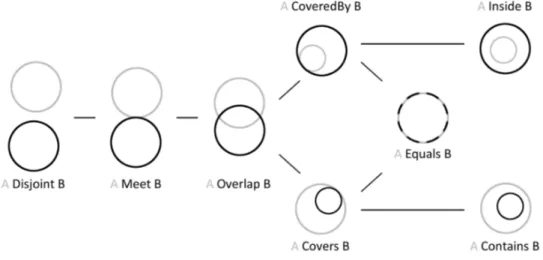
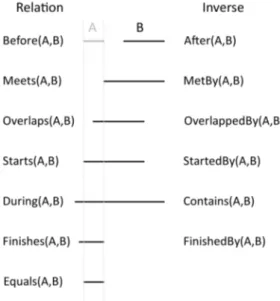
As we will see in the next sections, in the archaeological domain the spatial location and/or extent of an object can be defined in different ways: sometimes it is possible to have
2 Until a refrigerator-stable vaccine becomes available, however, varicella vac- cine will not be incorporated into the recommend- ed immunization schedule in Canada, as most
Production is described using data coming from various sections of the ICCD schema, in which we find all the information to describe the creators and the techniques involved in
We overview the three tractable OWL fragments and discuss dramatic speed improvements achieved by corresponding specialized reasoners. Furthermore, various combinations of
Our domain expert 4 has modeled judicial reasoning for owners corporations cases heard by VCAT using an OWL ontology to capture the discrete areas of decision making and factors
However, to address real use cases for knowledge driven applications, it must also address a wider set of issues related to ontology engineering, ease of use,
• Step 2: For every unsatisfied concept, we identify a minimal subset axioms and facts that are responsible for an inconsistency, called Minimal Unsatisfied Preserving Sub